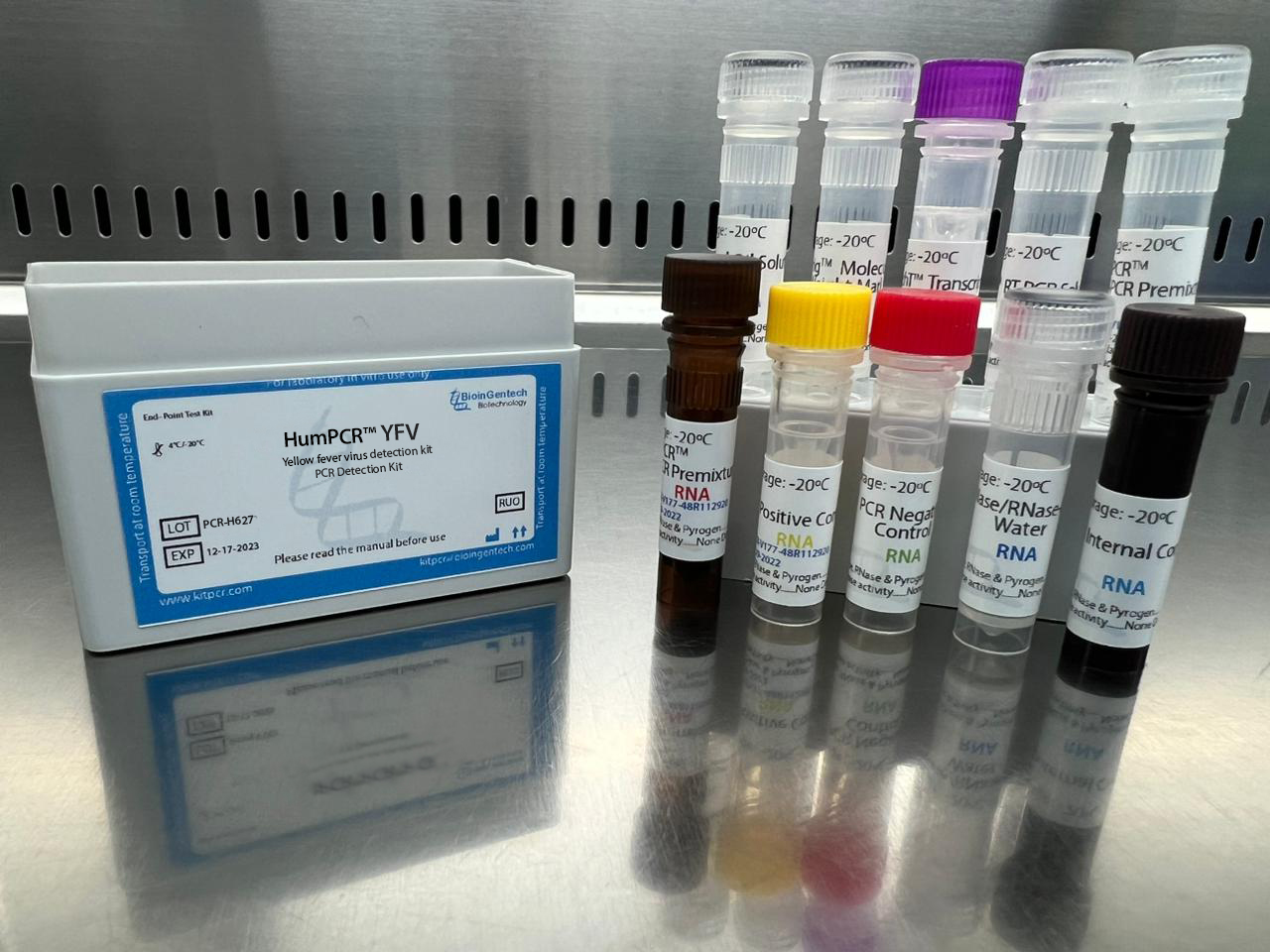
Yellow fever virus detection kits
| End-Point | 48 – 96 reactions |
| One-Step | 50 – 100 – 150 reactions |
Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes currently endemic in parts of equatorial Africa and South America, with previous circulation in parts of North America. It can be transmitted to humans through the bites of certain Aedes or Haemagogus species of mosquitoes and has distinct transmission cycles. The virus is an RNA virus of the genus Flavivirus. The viruses infect, amongst others, monocytes, macrophages, schwann cells, and dendritic cells. They attach to the cell surfaces via specific receptors and are taken up by an endosomal vesicle. Inside the endosome, the decreased pH induces the fusion of the endosomal membrane with the virus envelope. The capsid enters the cytosol, decays, and releases the genome.
Symptoms of yellow fever include fever, headache, jaundice, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting and fatigue.
Vaccination is the most important means of preventing yellow fever. The yellow fever vaccine is safe, affordable and a single dose provides life-long protection against yellow fever disease.
| End-Point | MANUAL | MSDS |
| One-Step | MANUAL | MSDS |
Related products
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory