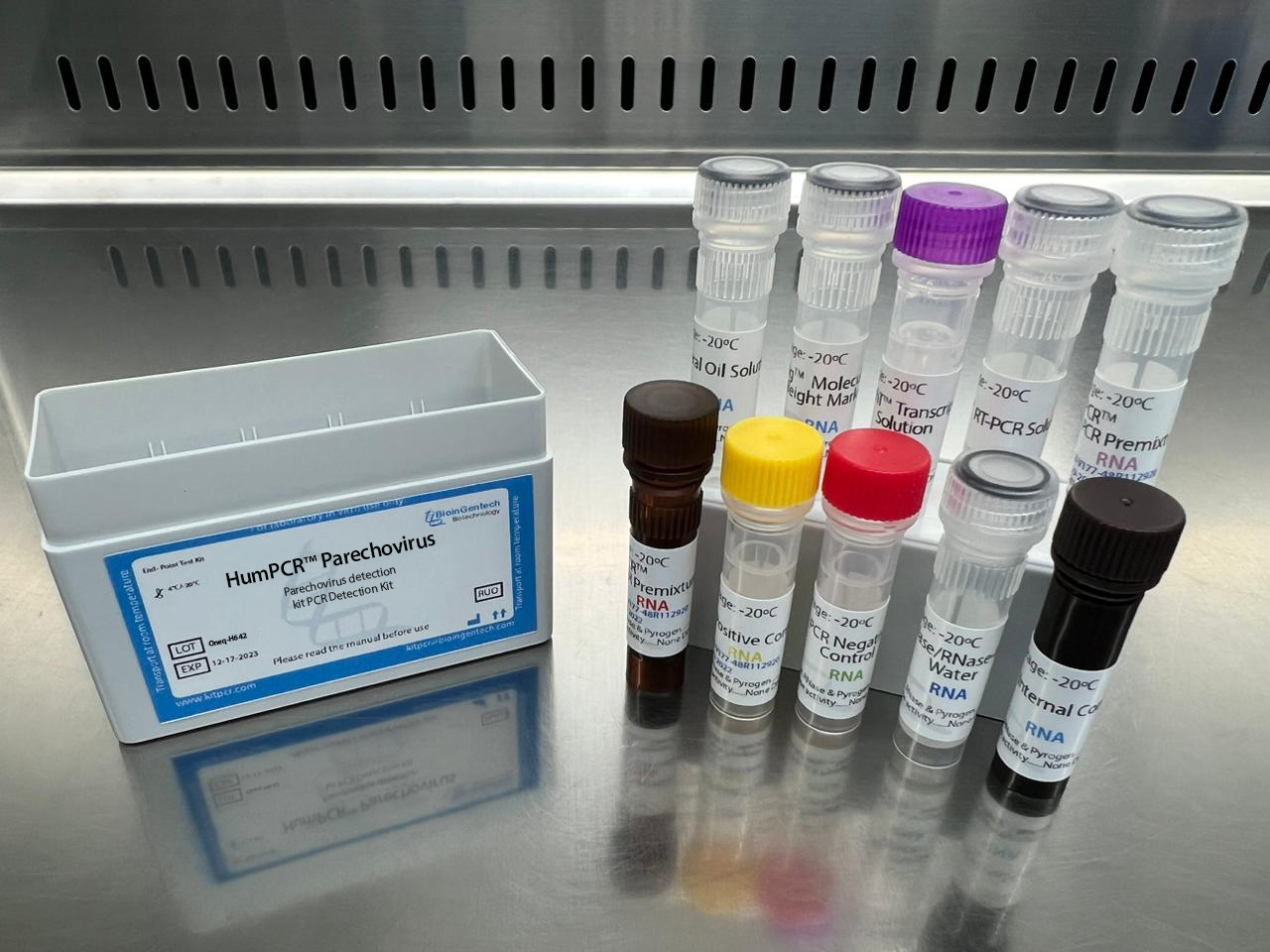
Parechovirus detection kits
| End-Point | 48 – 96 reactions |
| One-Step | 50 – 100 – 150 reactions |
Human parechoviruses (HPeVs) have recently been recognized to cause a variety of symptoms ranging from mild diarrhea to sepsis and meningitis, particularly among young children. HPeVs belong to a large family of nonenveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses, the Picornaviridae. Human parechoviruses (HPeVs) usually cause no symptoms at all but when illness occurs it is most commonly a mild diarrheal illness or respiratory infection. Infection with some strains can, rarely, lead to more severe blood infection (sepsis) and neurological infection (meningitis or encephalitis), particularly among young children. Parechovirus is usually spread from person to person through contact with respiratory droplets, saliva or faeces from an infected person.
| End-Point | MANUAL | MSDS |
| One-Step | MANUAL | MSDS |
Related products
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory
Respiratory