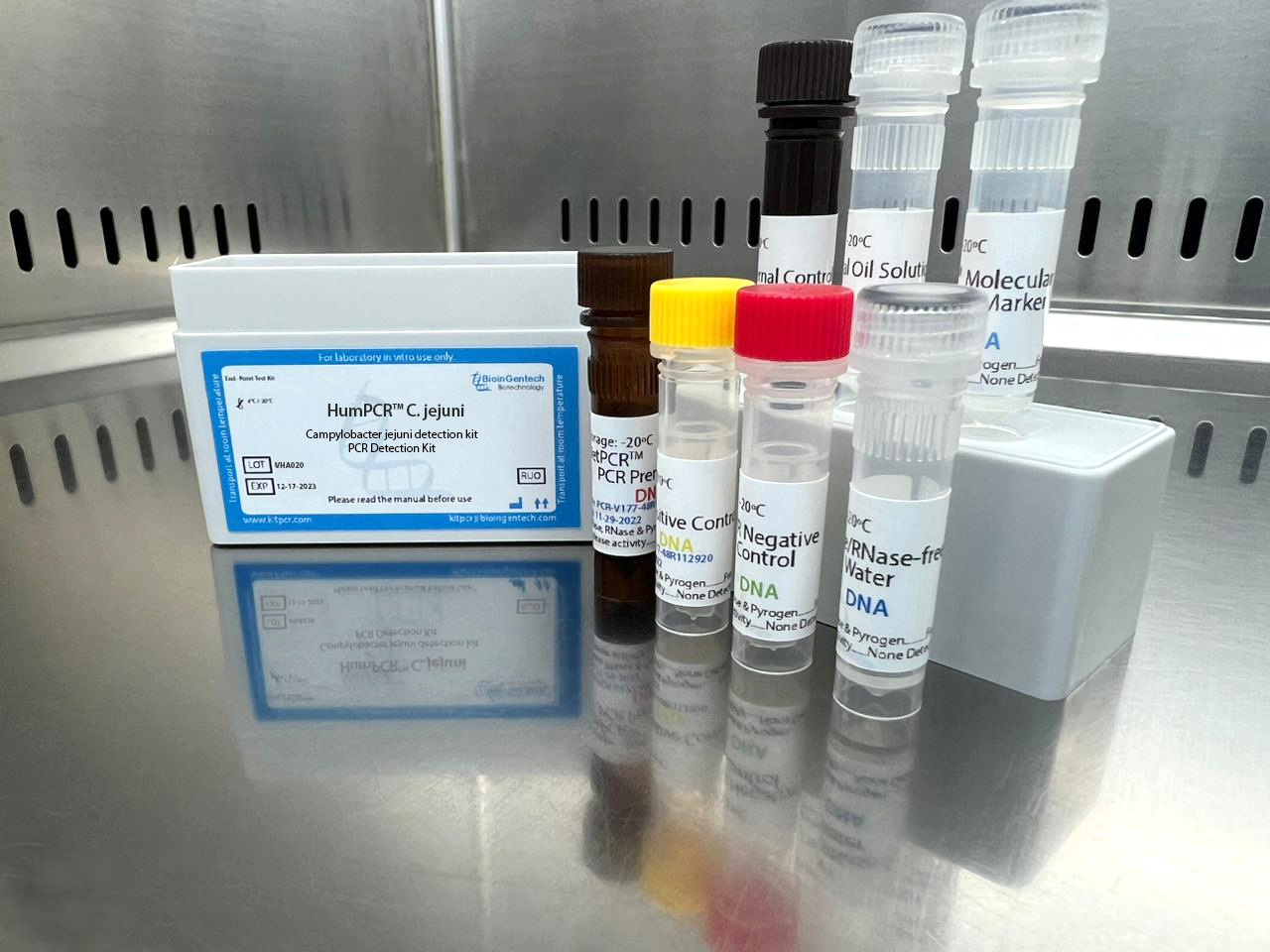
Campylobacter jejuni detection kits
| End-Point | 48 – 96 reactions |
| One-Step | 50 – 100 – 150 reactions |
Campylobacter is a leading cause of bacterial diarrheal disease worldwide. Most infections are caused by Campylobacter jejuni. C. jejuni is carried normally in the intestinal tracts of many domestic and wild animals. The disease is characterized by fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and occasionally, nausea, and vomiting. More severe presentations can occur, including bloodstream infection and disease mimicking acute appendicitis or ulcerative colitis. C. jejuni infection can trigger Guillain-Barré syndrome. The major modes of transmission include eating contaminated foods (especially undercooked chicken and foods contaminated by raw chicken), drinking raw milk or contaminated water, or having contact with animals, particularly farm animals such as poultry, sheep, and cattle, as well as cats and dogs.
| End-Point | MANUAL | MSDS |
| One-Step | MANUAL | MSDS |
Related products
Neurology
Neurology
Neurology
Neurology
Neurology
Neurology
Neurology